
Ontario Cancer Statistics 2020 Ch 7: Cancer Survival
Relative survival measures the likelihood of a person diagnosed with cancer surviving for a certain amount of time compared with similar people in the general population. This chapter focuses on 5-year relative cancer survival for adults and overall cancer survival proportion for children in Ontario.
What's on this page
Survival statistics are a key indicator of prognosis, and the effectiveness of control programs and cancer treatment.[1] Relative survival ratios (RSRs) show the likelihood of surviving for a certain amount of time (e.g., 1, 3 or 5 years) after diagnosis compared with similar people (i.e., same age and sex) in the general population.
The first 5 years after diagnosis are critical for examining survival. This is when someone is most likely to access healthcare services, including primary treatment, and clinical assessment for recurrence. After 5 years, use of the healthcare system and the chance of recurrence both decrease.
Cancer survival depends on factors including the cancer type, sex, age at diagnosis, stage at diagnosis and the type of treatment received. While RSRs represent the average survival expected for the population of people with a certain type of cancer, these statistics may not reflect the prognosis of an individual. A person’s survival can also depend on their health status, the presence of comorbidities, and other personal and tumour-related factors. Survival estimates are based on data from people diagnosed in the past. That means they may not reflect the impact of more recent advances in cancer detection and treatment. Relative survival also does not distinguish between people who have no evidence of cancer and those who have relapsed or are still in treatment.
Survival improves over time because of better methods for (and the greater use of) early detection, as well as more effective treatments. Even small improvements in survival rates can, at the population level, represent large numbers of people who avoided premature deaths.[2] Improvements in survival may also be the result of increased incidence through improved early detection. Catching cancers earlier than they would normally be found results in a “lead time bias.”[3] This bias results in potentially detecting cancers that would never have caused harm if left untreated (i.e., overdiagnosis).
Survival by Sex and Cancer Type
From 2012 to 2016, the 5-year relative survival ratio (RSR) for all cancers combined was 66.4% (Table 7.1). This means people diagnosed with cancer during this period were 66.4% as likely to survive at least 5 years after diagnosis compared with similar people without cancer in the general population.
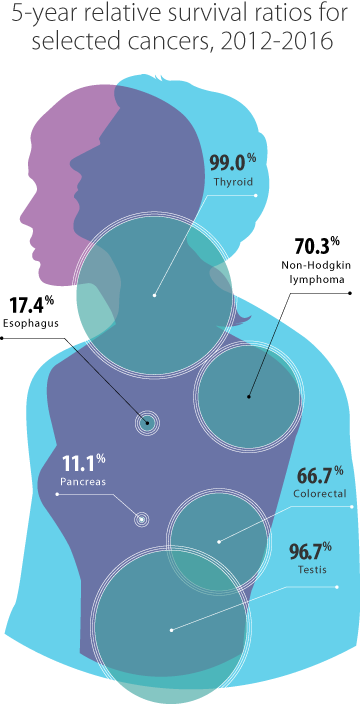
For cancer types that occur in both sexes, 5-year survival was:
- highest for thyroid cancer (99.0%), melanoma (88.0%) and Hodgkin lymphoma (86.2%)
- lowest for pancreatic (11.1%), esophageal (17.4%), lung (22.2%) and liver (23.3%) cancers, mainly because most cases of these cancers are diagnosed at an advanced stage[4,5]
People diagnosed with cancer were 66.4% as likely to survive at least 5 years after diagnosis compared with similar people in the general population.
For cancers with high mortality rates (particularly pancreatic cancer), relative survival estimates are generally higher in Ontario than in other provinces. This may be because of differences in survival methodology. Ontario’s methodology assumes that patients who are lost to follow-up are still alive at the cut-off date (5 years after diagnosis). This may result in overestimation of survival.[6] For high-mortality cancers, being alive longer than 5 years is very unlikely. This is particularly a problem for Ontario because evidence shows that the loss to follow-up rate is higher in Ontario than in other provinces. The reasons for this are unclear. Therefore, survival estimates for pancreatic, esophageal, liver and lung cancers should be interpreted with caution, especially when comparing with other jurisdictions.
There was wide variation in 5-year RSR for the following cancers (Table 7.1):
- malignant compared with non-malignant brain cancers
- subtypes of leukemia
- cutaneous compared with non-cutaneous melanoma
- endometrial compared with uterine sarcoma
- small cell compared with other types of lung cancer
Male survival during this period was significantly lower than female: 64.3% compared with 68.3%, a gap that has been widening over time. This difference likely results from generally higher survival rates in females than males for cancer types common in both sexes — particularly lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer death in Ontario.
For males, 5-year survival was:
- highest for thyroid (97.9%), testicular (96.7%) and prostate (94.2%) cancers
- lowest for pancreatic (11.0%), esophageal (17.4%) and lung (18.6%) cancers
For females, 5-year survival was:
- highest for thyroid cancer (99.2%), melanoma (92.0%) and breast cancer (88.7%)
- lowest for pancreatic (11.1%), esophageal (17.2%) and liver (22.0%) cancers
| Cancer type | Both sexes | Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSR | 95% CI | RSR | 95% CI | RSR | 95% CI | |
| All cancers | 66.4 | 66.1 - 66.6 | 64.3 | 63.9 - 64.7 | 68.3 | 68.0 - 68.7 |
| Brain and nervous system | ||||||
| Brain and other nervous system - Malignant | 28.0 | 26.2 - 29.8 | 27.3 | 25 - 29.7 | 28.9 | 26.2 - 31.6 |
| Glioblastoma | 5.6 | 4.5 - 7.0 | 4.8 | 3.4 - 6.6 | 6.7 | 4.8 - 9.1 |
| Meninges - malignant | 47.3 | 31.4 - 61.6 | 37.6 | 15.8 - 59.6 | 54.0 | 32.4 - 71.4 |
| Brain and other nervous system - Non-malignant | 85.3 | 84.1 - 86.4 | 84.1 | 82.1 - 85.9 | 86.1 | 84.5 - 87.5 |
| Meninges - nonmalignant | 85.0 | 82.9 - 86.8 | 82.1 | 77.9 - 85.5 | 86.3 | 83.9 - 88.4 |
| Pituitary, pineal and craniopharyngeal duct | 91.9 | 89.6 - 93.6 | 91.0 | 87.3 - 93.6 | 92.7 | 89.7 - 94.8 |
| Breast and genital system | ||||||
| Breast (female) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 88.7 | 88.2 - 89.2 |
| Cervix | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 68.6 | 65.6 - 71.4 |
| Ovary | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 46.8 | 44.7 - 48.8 |
| Prostate | n/a | n/a | 94.2 | 93.6 - 94.8 | n/a | n/a |
| Testis | n/a | n/a | 96.7 | 95.2 - 97.7 | n/a | n/a |
| Uterine | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 82.8 | 81.6 - 83.9 |
| Uterus - endometrial | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 85.8 | 84.6 - 86.9 |
| Uterus - uterine sarcoma | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 41.6 | 33.9 - 49.1 |
| Digestive system | ||||||
| Colorectal | 66.7 | 65.8 - 67.5 | 66.8 | 65.6 - 67.9 | 66.6 | 65.3 - 67.8 |
| Colon excluding rectum | 65.9 | 64.8 - 66.9 | 66.2 | 64.7 - 67.7 | 65.5 | 64.0 - 67.0 |
| Colon - left sided | 70.1 | 68.4 - 71.7 | 70.3 | 68.1 - 72.5 | 69.6 | 67.2 - 72.0 |
| Colon - right sided | 66.9 | 65.5 - 68.3 | 66.1 | 64.0 - 68.1 | 67.5 | 65.6 - 69.4 |
| Rectum and rectosigmoid junction | 68.6 | 67.2 - 70.0 | 68.0 | 66.2 - 69.8 | 69.5 | 67.3 - 71.7 |
| Rectosigmoid junction | 64.1 | 61.3 - 66.7 | 65.0 | 61.3 - 68.4 | 62.8 | 58.4 - 66.8 |
| Rectum | 70.3 | 68.6 - 71.9 | 69.2 | 67.0 - 71.3 | 72.1 | 69.4 - 74.6 |
| Esophagus | 17.4 | 15.4 - 19.4 | 17.4 | 15.1 - 19.8 | 17.2 | 13.4 - 21.3 |
| Esophagus - adenocarcinoma | 19.2 | 16.6 - 21.9 | 19.3 | 16.5 - 22.4 | 18.6 | 12.7 - 25.5 |
| Esophagus - squamous cell carcinoma | 15.8 | 12.5 - 19.5 | 14.9 | 10.8 - 19.6 | 17.1 | 11.8 - 23.3 |
| Liver | 23.3 | 21.6 - 25.1 | 23.8 | 21.7 - 25.9 | 22.0 | 19.0 - 25.2 |
| Pancreas | 11.1 | 10.0 - 12.1 | 11.0 | 9.5 - 12.5 | 11.1 | 9.7 - 12.6 |
| Stomach | 33.0 | 31.1 - 34.8 | 30.5 | 28.3 - 32.8 | 37.3 | 34.2 - 40.4 |
| Head and neck | ||||||
| Larynx | 67.3 | 63.4 - 70.9 | 69.2 | 64.9 - 73.1 | 57.5 | 47.8 - 66.0 |
| Oral cavity and pharynx | 63.1 | 61.3 - 64.8 | 62.9 | 60.8 - 65.0 | 63.5 | 60.1 - 66.7 |
| Lip and oral cavity | 64.3 | 61.7 - 66.8 | 63.2 | 59.8 - 66.4 | 66.2 | 61.7 - 70.2 |
| Hypopharynx | 33.0 | 26.0 - 40.2 | 32.0 | 24.4 - 39.7 | 39.4 | 20.7 - 57.7 |
| Nasopharynx | 66.4 | 59.7 - 72.2 | 63.0 | 54.9 - 70.0 | 75.0 | 61.7 - 84.2 |
| Oropharynx | 67.6 | 64.7 - 70.4 | 68.3 | 65.0 - 71.4 | 64.7 | 58.0 - 70.7 |
| Thyroid | 99.0 | 98.6 - 99.2 | 97.9 | 96.5 - 98.8 | 99.2 | 98.9 - 99.5 |
| Thyroid - anaplastic | 7.0 | 1.8 - 17.0 | ** | ** | 9.3 | 1.7 - 25.0 |
| Thyroid - follicular | 96.7 | 91.0 - 98.8 | 94.1 | 76.8 - 98.6 | 97.4 | 89.6 - 99.4 |
| Thyroid - medullary | 84.9 | 73.4 - 91.7 | 82.0 | 61.7 - 92.1 | 86.3 | 70.3 - 94.0 |
| Thyroid - papillary | 100.0 | 92.8 - 100.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 - 100.0 | 99.9 | 99.5 - 100.0 |
| Hematological | ||||||
| Leukemia | 64.4 | 62.9 - 65.9 | 64.8 | 62.7 - 66.7 | 63.9 | 61.5 - 66.1 |
| Acute lymphocytic leukemia | 74.3 | 70.1 - 78.0 | 76.0 | 70.5 - 80.6 | 71.8 | 65.0 - 77.5 |
| Acute monocytic leukemia | 18.7 | 11.9 - 26.7 | 17.7 | 8.8 - 29.1 | 20.7 | 11.1 - 32.4 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 25.2 | 22.6 - 27.9 | 24.7 | 21.2 - 28.4 | 25.9 | 22.1 - 29.8 |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 88.9 | 86.5 - 90.9 | 87.3 | 84.1 - 89.9 | 91.4 | 87.6 - 94.1 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 63.6 | 59.2 - 67.6 | 61.0 | 55.1 - 66.4 | 67.0 | 60.4 - 72.8 |
| Lymphoma | 71.9 | 70.8 - 72.9 | 71.5 | 70.0 - 72.9 | 72.3 | 70.8 - 73.9 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 86.2 | 83.6 - 88.5 | 87.2 | 83.7 - 90.1 | 85.0 | 80.9 - 88.3 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 70.3 | 69.2 - 71.4 | 69.8 | 68.2 - 71.3 | 70.9 | 69.2 - 72.5 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - extranodal | 72.0 | 70.3 - 73.6 | 72.9 | 70.6 - 75.1 | 70.8 | 68.3 - 73.2 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - nodal | 68.7 | 67.1 - 70.3 | 66.9 | 64.7 - 69.0 | 70.9 | 68.6 - 73.2 |
| Myeloma | 51.0 | 48.8 - 53.2 | 50.0 | 47.0 - 52.9 | 52.4 | 49.0 - 55.6 |
| Melanoma | ||||||
| Melanoma of the skin | 88.0 | 86.9 - 89.1 | 84.6 | 82.8 - 86.1 | 92.0 | 90.5 - 93.3 |
| Melanoma (non-cutaneous) | 69.4 | 63.3 - 74.6 | 71.3 | 62.2 - 78.6 | 67.3 | 58.8 - 74.4 |
| Melanoma - mucosal | 44.9 | 32.3 - 56.8 | 41.1 | 16.2 - 64.8 | 45.1 | 30.4 - 58.7 |
| Melanoma - ocular | 76.4 | 69.7 - 81.8 | 75.4 | 65.7 - 82.7 | 77.3 | 67.3 - 84.6 |
| Thoracic system | ||||||
| Lung | 22.2 | 21.5 - 22.8 | 18.6 | 17.8 - 19.4 | 25.7 | 24.8 - 26.6 |
| Lung - adenocarcinoma | 30.2 | 29.1 - 31.3 | 25.3 | 23.7 - 26.8 | 34.2 | 32.7 - 35.6 |
| Lung - large cell | 21.1 | 16.7 - 25.9 | 16.4 | 11.4 - 22.2 | 27.7 | 20.1 - 35.9 |
| Lung - small cell | 7.8 | 6.7 - 9.0 | 6.5 | 5.1 - 8.2 | 9.0 | 7.4 - 10.8 |
| Lung - squamous cell | 22.5 | 21.0 - 24.0 | 20.3 | 18.5 - 22.2 | 26.2 | 23.6 - 28.9 |
| Urinary system | ||||||
| Bladder | 77.9 | 76.6 - 79.0 | 78.8 | 77.3 - 80.2 | 75.0 | 72.5 - 77.2 |
| Kidney | 77.2 | 75.7 - 78.6 | 77.4 | 75.5 - 79.1 | 76.8 | 74.4 - 79.0 |
Abbreviations: CI means confidence interval; RSR means relative survival ratio.
Symbols:
- **Estimate could not be calculated.
- † Estimate is unreliable.
Note: The analysis was restricted to people ages 15 to 99.
Analysis by: Surveillance, Analytics and Informatics, Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
Data source: Ontario Cancer Registry (December 2018), Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
There were significant differences between males and females in 5-year survival for the following cancer types:
- Lung cancer survival was significantly higher in females (25.7%) than males (18.6%). Reasons may include the fact that males are more likely to have more aggressive lung cancer types, which have lower survival and are more likely to be diagnosed at a later stage.[7-9]
- Survival for melanoma was significantly higher in females (92.0%) than males (84.6%). Lower survival among males has been attributed to biological differences that make the cancer more likely to spread in males than in females.[10-12] Recent research has also suggested the expression of the PR70 protein, which is linked to the X-chromosome and expressed in higher doses among females, may suppress melanoma tumours.[13]
- Lower bladder cancer survival in females (75.0% versus 78.8% in males) may be because:
- females are typically diagnosed at a more advanced stage than males
- differences exist between the sexes in their ability to metabolize carcinogens
- there is a greater presence of sex steroids in females that could affect the progression of the cancer[14,15]
Survival by Age
Between 1982 to 1986 and 2012 to 2016, the 5-year age-standardized relative survival ratio (RSR) for all ages and cancers combined rose from 48.5% to 64.8% (Figure 7.1).
As in previous periods, the 5-year RSR for all cancers combined in 2012 to 2016 decreased with advancing age. For example, the RSR was 87.9% for people diagnosed from ages 15 to 39, but just 43.3% for those diagnosed from 80 to 99 years of age.
People diagnosed from ages 80 to 99 have seen little improvement in 5-year survival since the 1982 to 1986 period. As a result, the gap in survival between this age group and the younger age groups has widened over time. The greater improvements in survival among people under the age of 80 years may be the result of greater participation over time in screening programs for cervical, breast and colorectal cancers, and improved treatments available to them.[16]
The RSR for all cancers combined in Ontario has been increasing each decade since 1982, but the rate of increase has dropped over the most recent decade compared with previous periods. More specifically, of the 16.3 percentage point increase between 1982 and 2016, the largest improvement in survival occurred between 1982 to 1986 and 1992 to 1996 (7.1 percentage points) compared with only 2.5 percentage points between 2002 to 2006 and 2012 to 2016 (Table 7.2).
In Ontario, 85.7% of children 0 to 14 years of age diagnosed with cancer in 2016 were estimated to survive 5 years (i.e., 5-year overall survival proportion). Overall survival proportions are an estimate of the probability of surviving all causes of death. Children with cancer continued to experience gains in survival, with the 5-year overall survival proportion increasing from 76.0% in 1987 to 1991 to 85.3% in the latest 5-year period (2012 to 2016) (see Spotlight: Childhood Cancer Survival Trend, Figure 7.S1).
For details about childhood cancer survival trends, visit the POGO Surveillance Report .
Spotlight: Childhood Cancer Survival Trend
Survival Trends by Cancer Type
Between the periods of 1982 to 1986 and 2012 to 2016, gains in survival were greatest for the following cancers:
- prostate (22.8 percentage points)
- colorectal and its sub-sites (17.2)
- nasopharynx (17.5) and oropharynx (27.3)
- hematological cancers, including leukemia and several subtypes (26.0)
- lymphoma (20.7) and its subtypes
- myeloma (24.2)
- kidney cancer (27.0)
Notable increases are also seen for:
- breast (15.3)
- liver (14.2)
- stomach (13.6)
- ovary (11.3)
- medullary thyroid (15.5)
Smaller gains in survival occurred for cervical, endometrial and laryngeal cancers, and melanoma of the skin.
A downward trend in survival was observed for:
- bladder (11.1 percentage points decline)
- mucosal melanoma (25.9)
- lip and oral cavity (7.9)
When comparing sub-sites of colorectal cancer, the rectal cancer survival rate has increased since the period of 1982 to 1986 and is now comparable to survival for colon cancer. Similarly, survival for sub-sites of oral cavity & pharynx cancers are now more comparable than in the past with the exception of hypopharynx. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma survival is approaching the survival of Hodgkin lymphoma, even though Hodgkin lymphoma still has a higher 5-year RSR.
| Cancer type | 1982 - 1986 | 1992 - 1996 | 2002 - 2006 | 2012 - 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | |
| All cancers | 48.5 | 48.2 - 48.8 | 55.6 | 55.4 - 55.9 | 62.4 | 62.2 - 62.6 | 64.9 | 64.6 - 65.2 |
| Brain and nervous system | ||||||||
| Brain and other nervous system - Malignant | 24.9 | 23.5 - 26.4 | 30.3 | 28.9 - 31.8 | 32.9 | 31.6 - 34.3 | 29.8 | 28.1 - 31.5 |
| Glioblastoma | 6.6 | 4.9 - 8.7 | 8.6 | 6.9 - 10.5 | 8.8 | 7.0 - 10.9 | 11.0 | 8.3 - 14.0 |
| Meninges - malignant | 61.9 | 50.5 - 71.4 | 71.2 | 63.5 - 77.7 | 57.1 | 47.6 - 65.5 | 48.5 | 31.7 - 63.3 |
| Brain and other nervous system - Non-malignant | † | † | † | † | † | † | † | † |
| Meninges - nonmalignant | † | † | † | † | † | † | † | † |
| Pituitary, pineal and craniopharyngeal duct | † | † | † | † | † | † | † | † |
| Breast and genital system | ||||||||
| Breast (female) | 73.0 | 72.1 - 73.8 | 82.5 | 81.9 - 83.2 | 86.3 | 85.7 - 86.9 | 88.3 | 87.6 - 89.0 |
| Cervix | 65.3 | 63.2 - 67.3 | 67.2 | 65.1 - 69.2 | 66.1 | 63.8 - 68.3 | 66.4 | 63.3 - 69.3 |
| Ovary | 30.2 | 28.4 - 31.9 | 36.1 | 34.5 - 37.8 | 39.8 | 38.4 - 41.3 | 41.5 | 39.5 - 43.5 |
| Prostate | 70.4 | 69.0 - 71.7 | 86.2 | 85.4 - 86.9 | 95.5 | 95.0 - 96.0 | 93.2 | 92.5 - 93.8 |
| Testis | 85.1 | 80.0 - 88.9 | 91.8 | 88.1 - 94.4 | 94.1 | 90.3 - 96.4 | 91.1 | 82.1 - 95.7 |
| Uterine | 79.7 | 78.0 - 81.4 | 82.7 | 81.2 - 84.1 | 81.6 | 80.3 - 82.9 | 79.8 | 78.3 - 81.2 |
| Uterus - endometrial | 82.2 | 80.3 - 83.9 | 85.1 | 83.6 - 86.6 | 84.5 | 83.2 - 85.7 | 83.1 | 81.6 - 84.5 |
| Uterus - uterine sarcoma | 36.6 | 26.6 - 46.6 | 40.7 | 32.9 - 48.4 | 47.0 | 38.1 - 55.4 | 35.3 | 25.5 - 45.3 |
| Digestive system | ||||||||
| Colorectal | 50.7 | 49.9 - 51.5 | 55.5 | 54.8 - 56.2 | 63.2 | 62.6 - 63.8 | 67.9 | 67.1 - 68.7 |
| Colon excluding rectum | 52.7 | 51.8 - 53.7 | 56.3 | 55.5 - 57.2 | 63.5 | 62.7 - 64.2 | 67.4 | 66.4 - 68.4 |
| Colon - left sided | 54.0 | 52.4 - 55.5 | 59.3 | 57.9 - 60.6 | 67.1 | 65.9 - 68.3 | 70.7 | 69.1 - 72.3 |
| Colon - right sided | 52.6 | 51.2 - 54.1 | 56.2 | 54.9 - 57.5 | 62.8 | 61.7 - 63.8 | 67.4 | 66.0 - 68.8 |
| Rectum and rectosigmoid junction | 47.0 | 45.6 - 48.4 | 54.6 | 53.3 - 55.9 | 63.0 | 61.9 - 64.0 | 68.1 | 66.7 - 69.5 |
| Rectosigmoid junction | 42.2 | 39.3 - 45.0 | 54.7 | 52.4 - 57.0 | 60.6 | 58.7 - 62.5 | 64.3 | 61.5 - 66.9 |
| Rectum | 48.4 | 46.7 - 50.0 | 54.4 | 52.8 - 55.9 | 63.9 | 62.6 - 65.2 | 69.5 | 67.8 - 71.2 |
| Esophagus | 13.2 | 11.2 - 15.2 | 14.5 | 12.9 - 16.3 | 16.1 | 14.6 - 17.7 | 19.5 | 17.3 - 21.8 |
| Esophagus - adenocarcinoma | 13.1 | 9.5 - 17.4 | 13.2 | 10.7 - 15.9 | 15.0 | 13.1 - 17.1 | 20.9 | 18.2 - 23.8 |
| Esophagus - squamous cell carcinoma | 12.8 | 10.3 - 15.6 | 16.0 | 13.4 - 18.8 | 17.1 | 14.5 - 19.9 | † | † |
| Liver | 8.9 | 6.8 - 11.2 | 12.3 | 10.6 - 14.2 | 21.9 | 20.3 - 23.6 | 23.1 | 21.3 - 25.0 |
| Pancreas | 7.2 | 6.3 - 8.2 | 8.4 | 7.5 - 9.3 | 11.1 | 10.2 - 12.0 | 13.0 | 11.8 - 14.2 |
| Stomach | 21.0 | 19.7 - 22.4 | 23.0 | 21.7 - 24.3 | 27.8 | 26.5 - 29.1 | 34.6 | 32.8 - 36.5 |
| Head and neck | ||||||||
| Larynx | 65.3 | 61.9 - 68.5 | 63.0 | 60.0 - 65.8 | 64.6 | 61.8 - 67.2 | 66.7 | 62.5 - 70.4 |
| Oral cavity & pharynx | 57.2 | 55.1 - 59.1 | 57.2 | 55.4 - 59.0 | 58.6 | 56.9 - 60.3 | 60.1 | 58.2 - 62.0 |
| Lip and oral cavity | 71.3 | 68.7 - 73.8 | 68.8 | 66.3 - 71.1 | 66.3 | 63.9 - 68.5 | 63.4 | 60.7 - 66.1 |
| Hypopharynx | 23.7 | 18.8 - 28.9 | 25.7 | 21.0 - 30.7 | 32.4 | 26.8 - 38.2 | † | † |
| Nasopharynx | 45.6 | 38.8 - 52.2 | 58.1 | 52.7 - 63.1 | 62.6 | 57.5 - 67.1 | 63.1 | 56.6 - 68.9 |
| Oropharynx | 33.4 | 29.4 - 37.4 | 42.3 | 38.6 - 45.9 | 50.2 | 47.2 - 53.2 | 60.7 | 56.9 - 64.3 |
| Thyroid | 82.4 | 79.6 - 84.8 | 89.9 | 87.9 - 91.6 | 95.8 | 94.8 - 96.7 | 97.8 | 97.0 - 98.5 |
| Thyroid - anaplastic | 22.8 | 6.6 - 44.9 | 5.6 | 1.7 - 13 | 36.8 | 30.5 - 43.2 | † | † |
| Thyroid - follicular | 89.3 | 84.0 - 92.9 | 87.9 | 82.5 - 91.8 | 95.8 | 90.5 - 98.2 | 95.3 | 87.9 - 98.2 |
| Thyroid - medullary | 65.7 | 56.1 - 73.7 | 85.0 | 71.9 - 92.3 | 85.9 | 75.3 - 92.2 | 81.2 | 72.1 - 87.6 |
| Thyroid - papillary | 91.4 | 85.8 - 94.8 | 96.2 | 93 - 98 | 98.3 | 97.3 - 99.0 | 99.9 | 99.3 - 100.0 |
| Hematological | ||||||||
| Leukemia | 37.3 | 35.7 - 38.9 | 43.6 | 42.2 - 45.0 | 55.4 | 54.2 - 56.7 | 63.3 | 61.8 - 64.9 |
| Acute lymphocytic leukemia | 26.7 | 21.3 - 32.4 | 32.0 | 26.7 - 37.4 | 48.5 | 43.3 - 53.5 | 55.1 | 48.2 - 61.4 |
| Acute monocytic leukemia | 7.7 | 3.0 - 15.5 | 14.0 | 7.8 - 22.0 | 15.6 | 10.0 - 22.3 | 18.8 | 11.8 - 27.1 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 12.7 | 10.6 - 14.9 | 13.6 | 11.9 - 15.5 | 16.0 | 14.4 - 17.7 | 21.9 | 19.5 - 24.5 |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 64.0 | 61.2 - 66.6 | 71.4 | 69.1 - 73.5 | 80.4 | 78.7 - 81.9 | 89.2 | 86.9 - 91.0 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 27.9 | 23.9 - 32.1 | 32.2 | 28.7 - 35.8 | 56.5 | 52.7 - 60.2 | 62.8 | 58.7 - 66.6 |
| Lymphoma | 49.9 | 48.3 - 51.4 | 49.7 | 48.5 - 51.0 | 61.7 | 60.7 - 62.7 | 70.6 | 69.5 - 71.7 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 71.0 | 68.6 - 73.3 | 80.1 | 77.8 - 82.1 | 82.9 | 80.9 - 84.7 | 85.2 | 82.7 - 87.3 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 49.8 | 48.1 - 51.4 | 48.1 | 46.8 - 49.4 | 61.0 | 60.0 - 62.1 | 70.4 | 69.3 - 71.6 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - extranodal | 73.3 | 63.3 - 81.0 | 74.6 | 66.7 - 80.9 | 81.2 | 77.8 - 84.2 | 72.7 | 71.1 - 74.2 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - nodal | 48.6 | 46.9 - 50.3 | 46.8 | 45.5 - 48.1 | 58.8 | 57.7 - 59.9 | 68.2 | 66.6 - 69.8 |
| Myeloma | 30.4 | 28.2 - 32.6 | 35.8 | 33.8 - 37.7 | 44.1 | 42.4 - 45.8 | 54.6 | 52.5 - 56.6 |
| Melanoma | ||||||||
| Melanoma of the skin | 82.6 | 81.0 - 84.1 | 83.4 | 82.2 - 84.5 | 87.5 | 86.7 - 88.3 | 90.7 | 89.8 - 91.6 |
| Melanoma (non-cutaneous) | 76.6 | 71.1 - 81.2 | 83.3 | 78.3 - 87.3 | 80.9 | 76.9 - 84.3 | 69.0 | 62.3 - 74.8 |
| Melanoma - mucosal | 64.8 | 48.7 - 77.0 | 66.5 | 50.2 - 78.6 | 61.3 | 47.0 - 72.8 | 38.9 | 27.2 - 50.5 |
| Melanoma - ocular | 77.7 | 71.7 - 82.5 | 85.3 | 79.8 - 89.5 | 82.9 | 78.6 - 86.4 | 77.6 | 70.5 - 83.3 |
| Thoracic system | ||||||||
| Lung | 14.0 | 13.5 - 14.5 | 16.2 | 15.7 - 16.6 | 17.7 | 17.3 - 18.2 | 23.9 | 23.2 - 24.7 |
| Lung - adenocarcinoma | 19.0 | 17.7 - 20.4 | 21.2 | 20.2 - 22.3 | 24.1 | 23.2 - 25.0 | 30.4 | 29.2 - 31.6 |
| Lung - large cell | 10.7 | 8.8 - 12.8 | 8.4 | 7.0 - 10.1 | 13.3 | 11.2 - 15.4 | † | † |
| Lung - small cell | 6.2 | 5.0 - 7.5 | 7.7 | 6.6 - 8.8 | 7.1 | 6.2 - 8.1 | 7.7 | 6.3 - 9.3 |
| Lung - squamous cell | 17.2 | 16.1 - 18.4 | 18.6 | 17.5 - 19.8 | 21.5 | 20.1 - 22.9 | 22.2 | 19.7 - 24.8 |
| Urinary system | ||||||||
| Bladder | 75.0 | 73.6 - 76.3 | 73.8 | 72.5 - 75.1 | 70.5 | 69.3 - 71.6 | 63.9 | 62.1 - 65.7 |
| Kidney | 48.2 | 45.9 - 50.4 | 61.5 | 59.7 - 63.3 | 67.6 | 66.1 - 69.0 | 75.2 | 73.5 - 76.8 |
Abbreviations: CI means confidence interval; RSR means relative survival ratio.
Symbol: †Statistic could not be calculated
Notes:
- Analysis was restricted to ages 15 to 99.
- The period method was used to derive RSRs for the 2012 to 2016 period. The cohort method was used for all other periods.
- IARC/IACR multiple primary rules used when presenting trends over time.
- RSRs age-standardized using the International Cancer Survival Standards (ICSS).
Analysis by: Surveillance, Analytics and Informatics, Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
Data source: Ontario Cancer Registry (December 2018), Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
Survival by Duration
For 2012 to 2016, the relative survival ratio (RSR) for all cancers combined was 80.0% after 1 year, 66.5% after 5 years, 62.6% after 10 years and 60.7% after 15 years (Figure 7.2).
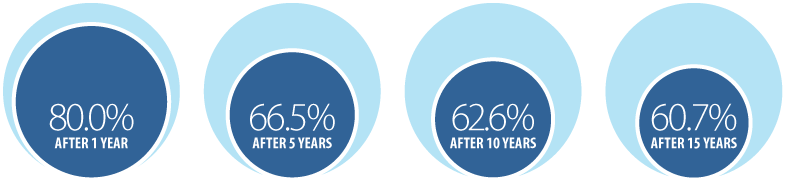
As with most individual cancer types, survival for all cancers combined declined most during the first year after diagnosis, followed by progressively smaller decreases in survival as the time from diagnosis increased. Some of the largest drops in survival in the first year after diagnosis were for brain, esophageal, liver, lung, myeloma, ovarian, pancreatic and stomach cancers.
For the 4 most common cancers, the following were observed for relative survival by duration:
- For breast cancer, the RSR 1 year after diagnosis was very high at 97.5%. At 5 years, the RSR fell to 88.9%. Survival at 10 and 15 years only decreased slightly to 84.0% and 80.6%, respectively.
- For colorectal cancer, the RSRs 1 year after diagnosis was 83.0% but fell to 66.9% at 5 years — a greater decrease than for breast cancer. There was no significant difference between the 10-year and 15-year RSRs for colorectal cancer.
- The greatest decrease in survival between 1 year and 5 years after diagnosis was for lung cancer, which fell from 48.5% to 22.2%. Survival continued to decrease significantly, to 16.1% at 10 years and 13.2% at 15 years.
- Prostate cancer survival decreased by a small, but significant, amount between 1 year and 5 years after diagnosis, but there was no significant difference between 5-year, 10-year and 15-year survival. In fact, the 5-year and 10-year RSRs were nearly the same (94.3% and 94.1%, respectively).
Survival by Stage
Stage at diagnosis is one of the most important predictors of cancer survival. Population-level stage data in Ontario is available from 2010 onward for the 4 most common cancers (breast, colorectal, lung and prostate) and cervical cancer, and for a limited number of years for thyroid cancer and melanoma. This section focuses on the most common cancers.
Five-year relative survival for 2012 to 2016 tended to decrease with advancing stage at diagnosis (Figure 7.3). The level of decrease varied by cancer type:
- While breast cancer cases diagnosed at stage 1 had a 5-year relative survival ratio (RSR) of 100.0%, the RSR decreased to just 27.1% for cases diagnosed at stage 4.
- Colorectal cancer cases diagnosed at stage 1 had a 5-year RSR of 92.3%, which declined to 85.4% for cases diagnosed at stage 2, 70.5% at stage 3 and just 13.2% at stage 4.
- Of the 4 most common cancers, lung cancer had the lowest survival at every stage. Even at stage 1, 5-year survival was just 66.0%, declining to 4.4% at stage 4.
- Stage at diagnosis had the least effect on prostate cancer. Five-year survival for stages 1 to 3 was equal or close to 100%; however, survival dipped to 45.9% for cases diagnosed at stage 4.
Five-year relative survival for 2012 to 2016 tended to decrease with advancing stage at diagnosis. The level of decrease varied by cancer type.
When examining only the screening program eligible age groups, breast and colorectal cancers showed the largest decline in 5-year survival between stage 3 and stage 4 cases (Figure 7.4). In contrast to breast and colorectal cancers, the largest decrease in survival from stage 1 (92.2%) to stage 2 (73.4%) was in cervical cancer.
Conditional Survival
Relative survival ratios (RSRs) represent the likelihood of surviving a specific number of years after diagnosis. However, sometimes it may be useful to measure survival starting at a time other than the date of diagnosis. Because people are more likely to die in the first year following diagnosis, survival after the first year (also called 1-year conditional survival) may be very different from survival measured at diagnosis. Table 7.3 presents survival at 5 years after diagnosis after already having survived 0 (the equivalent of non-conditional survival), 1, 2, 3 and 4 years.
While the 5-year RSR measured from diagnosis for all cancers combined for 2012 to 2016 was 66.4%, the 5-year RSR increased to 82.8% for those who survived the first year after diagnosis. The 5-year RSR increased for each year survived until 4 years after diagnosis, when it was 97.5%.
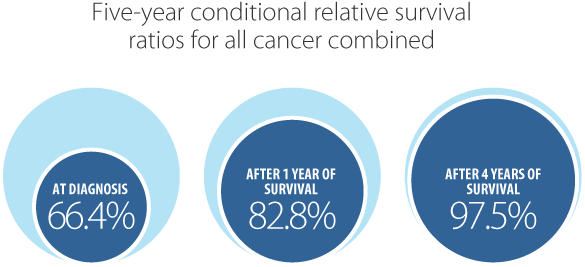
In general, once a person has survived the first year after diagnosis, their chance of surviving 5 years continues to increase, but the amount of increase gets smaller for each year they survive. For example, the 5-year survival for colorectal cancer increases by 13.5% after surviving the first year (66.7% to 80.2%), but only increases by 8% after surviving the second year (from 80.3% to 88.2%). Exceptions are for glioblastoma, endometrial cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, ocular melanoma and lung small cell carcinoma.
Cancers with poor prognosis (e.g., pancreatic, esophageal, liver, lung, stomach, brain) showed the highest relative gain after the first year in the chance of surviving. For example, while the 5-year RSR for pancreatic cancer was only 11.2% at diagnosis, it rose to 34.7% for those who survived their first year. Cancers with good prognosis (e.g., thyroid, testicular, prostate, breast) showed only a small difference in 1-year conditional RSR because survival at diagnosis is already high.
| Cancer type | 0 years survived† | 1 years survived | 2 years survived | 3 years survived | 4 years survived | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | RSR (%) | 95% CI | |
| All cancers | 66.4 | 66.1 - 66.6 | 82.8 | 82.5 - 83.0 | 89.8 | 89.6 - 90.0 | 94.4 | 94.2 - 94.5 | 97.5 | 97.4 - 97.6 |
| Brain and nervous system | ||||||||||
| Brain and other nervous system - Malignant | 28.0 | 26.2 - 29.8 | 51.3 | 48.7 - 54.0 | 73.9 | 71 - 76.5 | 86.4 | 83.8 - 88.6 | 94.2 | 92.2 - 95.7 |
| Glioblastoma | 5.6 | 4.5 - 7.0 | 13.7 | 10.8 - 16.8 | 33.3 | 26.9 - 39.7 | 57.6 | 48.0 - 66.0 | 78.6 | 68.2 - 86.0 |
| Meninges - malignant | 47.3 | 31.4 - 61.6 | 65.6 | 46.2 - 79.4 | 70.4 | 51.2 - 83.2 | 84.0 | 65.7 - 93.0 | 88.9 | 71.1 - 96.0 |
| Brain and other nervous system - Non-malignant | 85.3 | 84.1 - 86.4 | 94.0 | 93.0 - 94.9 | 95.9 | 95.0 - 96.7 | 97.7 | 96.9 - 98.2 | 98.4 | 97.8 - 98.8 |
| Meninges - nonmalignant | 85.0 | 82.9 - 86.8 | 92.4 | 90.5 - 94.0 | 94.2 | 92.4 - 95.5 | 96.1 | 94.6 - 97.2 | 97.2 | 96.0 - 98.0 |
| Pituitary, pineal and craniopharyngeal duct | 91.9 | 89.6 - 93.6 | 96.7 | 94.7 - 98.0 | 98.4 | 96.4 - 99.3 | 99.0 | 97.1 - 99.7 | 99.0 | 97.7 - 99.6 |
| Breast and genital system | ||||||||||
| Breast (female) | 88.7 | 88.2 - 89.2 | 91.0 | 90.5 - 91.5 | 93.1 | 92.7 - 93.6 | 95.8 | 95.4 - 96.2 | 97.7 | 97.4 - 98.0 |
| Cervix | 68.6 | 65.6 - 71.4 | 79.4 | 76.5 - 82.0 | 87.9 | 85.4 - 90.0 | 93.8 | 91.9 - 95.3 | 97.3 | 95.8 - 98.2 |
| Ovary | 46.8 | 44.7 - 48.8 | 59.8 | 57.4 - 62.0 | 71.6 | 69.2 - 73.8 | 81.2 | 78.9 - 83.3 | 91.6 | 89.8 - 93.2 |
| Prostate | 94.2 | 93.6 - 94.8 | 96.3 | 95.7 - 96.8 | 97.8 | 97.3 - 98.2 | 99.2 | 98.7 - 99.4 | 99.7 | 99.3 - 99.9 |
| Testis | 96.7 | 95.2 - 97.7 | 98.4 | 97.1 - 99.1 | 99.0 | 97.9 - 99.6 | 99.6 | 98.6 - 99.9 | 100.0 | 0.0 - 100.0 |
| Uterine | 82.8 | 81.6 - 83.9 | 88.8 | 87.7 - 89.8 | 92.7 | 91.7 - 93.5 | 96.3 | 95.5 - 97.0 | 98.6 | 98.0 - 99.0 |
| Uterus - endometrial | 85.8 | 84.6 - 86.9 | 90.1 | 89.0 - 91.1 | 93.4 | 92.5 - 94.3 | 96.6 | 95.8 - 97.3 | 98.7 | 98.1 - 99.1 |
| Uterus - uterine sarcoma | 41.6 | 33.9 - 49.1 | 53.7 | 44.4 - 62.1 | 67.2 | 56.8 - 75.7 | 84.1 | 74.2 - 90.5 | 93.3 | 85.1 - 97.1 |
| Digestive system | ||||||||||
| Colorectal | 66.7 | 65.8 - 67.5 | 80.2 | 79.4 - 81.1 | 87.2 | 86.4 - 87.9 | 92.6 | 91.9 - 93.2 | 96.8 | 96.3 - 97.2 |
| Colon excluding rectum | 65.9 | 64.8 - 66.9 | 81.0 | 80.0 - 82.1 | 88.2 | 87.3 - 89.2 | 93.4 | 92.5 - 94.1 | 97.2 | 96.5 - 97.7 |
| Colon - left sided | 70.1 | 68.4 - 71.7 | 81.6 | 80.0 - 83.1 | 87.8 | 86.3 - 89.1 | 92.8 | 91.5 - 93.9 | 96.8 | 95.8 - 97.5 |
| Colon - right sided | 66.9 | 65.5 - 68.3 | 81.4 | 79.9 - 82.7 | 89.0 | 87.6 - 90.2 | 93.9 | 92.8 - 94.9 | 97.5 | 96.6 - 98.1 |
| Rectum and rectosigmoid junction | 68.6 | 67.2 - 70.0 | 78.8 | 77.4 - 80.1 | 85.3 | 84.0 - 86.5 | 91.2 | 90.1 - 92.2 | 96.1 | 95.3 - 96.8 |
| Rectosigmoid junction | 64.1 | 61.3 - 66.7 | 76.3 | 73.5 - 78.9 | 82.8 | 80.2 - 85.1 | 88.2 | 85.8 - 90.1 | 95.0 | 93.1 - 96.3 |
| Rectum | 70.3 | 68.6 - 71.9 | 79.8 | 78.1 - 81.3 | 86.3 | 84.8 - 87.7 | 92.4 | 91.1 - 93.6 | 96.6 | 95.6 - 97.4 |
| Esophagus | 17.4 | 15.4 - 19.4 | 37.1 | 33.3 - 40.9 | 62.5 | 57.2 - 67.3 | 79.0 | 73.7 - 83.4 | 89.3 | 84.6 - 92.7 |
| Esophagus - adenocarcinoma | 19.2 | 16.6 - 21.9 | 37.6 | 32.9 - 42.2 | 63.2 | 56.7 - 69.0 | 81.5 | 74.8 - 86.6 | 91.6 | 85.6 - 95.1 |
| Esophagus - squamous cell carcinoma | 15.8 | 12.5 - 19.5 | 37.1 | 29.9 - 44.3 | 62.8 | 52.5 - 71.6 | 75.4 | 64.5 - 83.4 | 85.8 | 75.3 - 92.0 |
| Liver | 23.3 | 21.6 - 25.1 | 50.8 | 47.5 - 53.9 | 67.7 | 64.0 - 71.1 | 80.2 | 76.5 - 83.4 | 91.7 | 88.6 - 94.0 |
| Pancreas | 11.1 | 10.0 - 12.1 | 34.7 | 31.8 - 37.6 | 60.4 | 56.2 - 64.4 | 79.2 | 74.7 - 83.0 | 90.9 | 86.9 - 93.7 |
| Stomach | 33.0 | 31.1 - 34.8 | 59.2 | 56.5 - 61.9 | 77.6 | 74.7 - 80.2 | 88.0 | 85.4 - 90.2 | 93.8 | 91.6 - 95.4 |
| Head and neck | ||||||||||
| Larynx | 67.3 | 63.4 - 70.9 | 77.6 | 73.6 - 81.0 | 86.2 | 82.5 - 89.3 | 92.1 | 88.7 - 94.5 | 95.6 | 92.8 - 97.3 |
| Oral cavity and pharynx | 63.1 | 61.3 - 64.8 | 76.5 | 74.7 - 78.3 | 85.6 | 83.9 - 87.2 | 90.8 | 89.3 - 92.1 | 95.6 | 94.4 - 96.5 |
| Lip and oral cavity | 64.3 | 61.7 - 66.8 | 77.6 | 74.9 - 80.0 | 86.9 | 84.4 - 89.0 | 91.6 | 89.4 - 93.4 | 95.7 | 93.9 - 97.0 |
| Hypopharynx | 33.0 | 26.0 - 40.2 | 53.8 | 43.6 - 62.9 | 71.3 | 59.5 - 80.2 | 78.3 | 66.5 - 86.3 | 91.2 | 79.7 - 96.3 |
| Nasopharynx | 66.4 | 59.7 - 72.2 | 79.3 | 72.3 - 84.6 | 87.9 | 81.2 - 92.3 | 93.2 | 86.9 - 96.5 | 96.7 | 91.3 - 98.8 |
| Oropharynx | 67.6 | 64.7 - 70.4 | 79.1 | 76.1 - 81.7 | 86.6 | 83.7 - 88.9 | 91.4 | 88.8 - 93.4 | 96.4 | 94.4 - 97.7 |
| Thyroid | 99.0 | 98.6 - 99.2 | 99.9 | 99.4 - 100.0 | 100.0 | † | 99.9 | 99.0 - 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.6 - 100.0 |
| Thyroid - anaplastic | 7.0 | 1.8 - 17.0 | 29.6 | 7.5 - 56.4 | 49.5 | 13.6 - 78.1 | 83.6 | 26.8 - 97.6 | 100.0 | † |
| Thyroid - follicular | 96.7 | 91.0 - 98.8 | 98.1 | 91.7 - 99.6 | 99.1 | 89.4 - 99.9 | 98.3 | 93.8 - 99.5 | 99.7 | 94.4 - 100.0 |
| Thyroid - medullary | 84.9 | 73.4 - 91.7 | 88.0 | 76.5 - 94.1 | 90.4 | 78.8 - 95.8 | 94.4 | 83.2 - 98.2 | 97.8 | 86.0 - 99.7 |
| Thyroid - papillary | 100.0 | 92.8 - 100.0 | 100.0 | † | 100.0 | † | 100.0 | † | 100.0 | 98.2 - 100.0 |
| Hematological | ||||||||||
| Leukemia | 64.4 | 62.9 - 65.9 | 82.0 | 80.4 - 83.4 | 89.0 | 87.5 - 90.3 | 93.6 | 92.3 - 94.6 | 96.9 | 95.9 - 97.6 |
| Acute lymphocytic leukemia | 74.3 | 70.1 - 78.0 | 87.3 | 83.5 - 90.3 | 91.7 | 88.2 - 94.2 | 96.2 | 93.3 - 97.8 | 98.0 | 95.7 - 99.1 |
| Acute monocytic leukemia | 18.7 | 11.9 - 26.7 | 45.1 | 30.0 - 59.0 | 70.0 | 48.7 - 83.8 | 87.0 | 59.7 - 96.3 | 90.4 | 62.5 - 97.8 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 25.2 | 22.6 - 27.9 | 52.8 | 48.1 - 57.2 | 74.9 | 69.6 - 79.5 | 86.4 | 81.4 - 90.2 | 96.4 | 92.6 - 98.3 |
| Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | 88.9 | 86.5 - 90.9 | 92.4 | 90.1 - 94.2 | 93.6 | 91.4 - 95.3 | 95.2 | 93.3 - 96.6 | 97.1 | 95.5 - 98.1 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 63.6 | 59.2 - 67.6 | 75.4 | 70.9 - 79.3 | 83.3 | 79.0 - 86.8 | 90.8 | 87.0 - 93.6 | 94.1 | 90.9 - 96.3 |
| Lymphoma | 71.9 | 70.8 - 72.9 | 86.7 | 85.7 - 87.7 | 91.6 | 90.7 - 92.4 | 94.8 | 94.0 - 95.5 | 97.6 | 97.0 - 98.1 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 86.2 | 83.6 - 88.5 | 94.4 | 92.2 - 96.0 | 96.0 | 94.1 - 97.3 | 97.5 | 95.9 - 98.5 | 98.8 | 97.5 - 99.4 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 70.3 | 69.2 - 71.4 | 85.8 | 84.6 - 86.8 | 91.0 | 89.9 - 91.9 | 94.4 | 93.5 - 95.2 | 97.4 | 96.7 - 97.9 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - extranodal | 72.0 | 70.3 - 73.6 | 87.2 | 85.5 - 88.7 | 91.9 | 90.3 - 93.2 | 94.7 | 93.3 - 95.8 | 97.6 | 96.5 - 98.3 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma - nodal | 68.7 | 67.1 - 70.3 | 84.3 | 82.8 - 85.8 | 90.0 | 88.6 - 91.3 | 94.1 | 92.9 - 95.2 | 97.2 | 96.2 - 97.9 |
| Myeloma | 51.0 | 48.8 - 53.2 | 64.3 | 61.8 - 66.7 | 72.4 | 69.8 - 74.7 | 80.8 | 78.4 - 83.0 | 88.9 | 86.8 - 90.7 |
| Melanoma | ||||||||||
| Melanoma of the skin | 88.0 | 86.9 - 89.1 | 91.7 | 90.6 - 92.6 | 94.5 | 93.5 - 95.3 | 96.9 | 96.0 - 97.5 | 98.7 | 98.1 - 99.2 |
| Melanoma (non-cutaneous) | 69.4 | 63.3 - 74.6 | 74.0 | 68.0 - 79.1 | 81.1 | 75.2 - 85.7 | 88.9 | 83.5 - 92.6 | 93.9 | 89.3 - 96.6 |
| Melanoma - mucosal | 44.9 | 32.3 - 56.8 | 61.0 | 45.2 - 73.5 | 72.3 | 55 - 83.9 | 88.2 | 68.9 - 95.9 | 94.2 | 77.2 - 98.6 |
| Melanoma - ocular | 76.4 | 69.7 - 81.8 | 76.7 | 70.1 - 82 | 82.5 | 76.2 - 87.3 | 88.8 | 82.9 - 92.7 | 93.6 | 88.5 - 96.5 |
| Thoracic system | ||||||||||
| Lung | 22.2 | 21.5 - 22.8 | 46.7 | 45.6 - 47.9 | 64.9 | 63.6 - 66.2 | 79.3 | 78.0 - 80.5 | 90.7 | 89.6 - 91.7 |
| Lung - adenocarcinoma | 30.2 | 29.1 - 31.3 | 52.2 | 50.5 - 53.7 | 68.1 | 66.3 - 69.8 | 81.4 | 79.6 - 83.0 | 91.2 | 89.8 - 92.4 |
| Lung - large cell | 21.1 | 16.7 - 25.9 | 47.6 | 39.0 - 55.7 | 69.8 | 59.4 - 78.0 | 80.9 | 70.5 - 87.9 | 90.7 | 81.2 - 95.5 |
| Lung - small cell | 7.8 | 6.7 - 9.0 | 22.2 | 19.3 - 25.3 | 48.3 | 42.8 - 53.6 | 69.3 | 62.8 - 74.9 | 87.6 | 81.5 - 91.8 |
| Lung - squamous cell | 22.5 | 21.0 - 24.0 | 41.6 | 39.1 - 44.1 | 59.4 | 56.3 - 62.4 | 75.7 | 72.4 - 78.6 | 89.0 | 86.2 - 91.2 |
| Urinary system | ||||||||||
| Bladder | 77.9 | 76.6 - 79.0 | 86.7 | 85.5 - 87.8 | 91.3 | 90.3 - 92.3 | 94.5 | 93.6 - 95.3 | 97.9 | 97.2 - 98.4 |
| Kidney | 77.2 | 75.7 - 78.6 | 88.1 | 86.8 - 89.4 | 92.1 | 90.9 - 93.2 | 95.3 | 94.2 - 96.2 | 98 | 97.2 - 98.6 |
Abbreviations: CI means confidence interval; RSR means relative survival ratio.
Symbol: †Zero years survived is the equivalent of non–conditional survival.
Note: Analysis was restricted to ages 15 to 99.
Analysis by: Surveillance, Analytics and Informatics, Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
Data source: Ontario Cancer Registry (December 2018), Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario)
